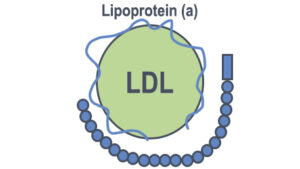
Unlock the potential of breakthrough lipoprotein(a) lowering drugs to improve your cardiovascular health and reduce your risk of heart disease. Lipoprotein(a) is a newer risk factor of heart disease similar to LDL cholesterol.

Currently, lipoprotein (a) lowering drugs have received great interest in the scientific community. The reason is the discovery that our blood serum contains another risk factor which is more dangerous than LDL cholesterol.
Lipoprotein(a) is also called lp(a) cholesterol. It has emerged as an independent risk factor for heart disease.
It is stickier compared to LDL cholesterol. It is 300 times more atherogenic than LDL cholesterol. If you are someone who is suffering from heart disease, now you have to rethink your strategy. Everyone who has risk factors for heart disease or wants to prevent or reverse heart attack must have a knowledge of lipoprotein(a), which is another newly discovered risk factor for heart disease.
Cause of elevated Lp(a) levels
One school of thought considers elevated lp(a) levels as due to genetic factors. More than 60 to 65% of the people are suffering from heart disease. Does this mean that all of them are suffering from heart disease due to genetic factors? It does not look so. The genetic defect in the world population is in the range of 2-3.4%.
Another school considers elevated lipoprotein(a) as the primary risk factor and not higher blood levels of LDL cholesterol. They have a valid reason to think so. Research has shown that the major constituent in the plaque consists of lp(a) cholesterol and less of LDL cholesterol, some amount of calcium deposit, and some amount of debris from the bloodstream. These studies have been published in US Patent.
Statins do not lower lipoprotein(a). Therefore, considerable scientific research is going on developing alternative drugs which can lower lipoprotein(a).
The future of prevention and reversal of heart disease depends upon lowering serum lipoprotein(a) levels and not lowering LDL cholesterol levels. Another important point to consider is the removal of plaque that has already been deposited in the arteries.
Statins do not remove plaque or LDL or Lp(a) deposited in the arteries. This is its greatest drawback.
Several breakthrough lipoprotein(a) lowering drugs have been developed. Some drugs have been approved for human use. Many drugs to lower lp(a) are in different stages of development. In this article, we will present all the information on these latest drugs.
The following table gives a list of drugs under different stages of development:
Table
Table of Contents
Lipoprotein(a) Lowering Drugs
| Name of Drug | Year | Company | Stage of Development |
| Pelacarsen (TQJ230) | 2023 | Ionis Pharmaceuticals/Akcea Therapeutics | Phase III Clinical Trials |
| Olpasiran (AMG890) | 2022 | Amgen | Phase III Clinical Trials |
| SLN360 | 2022 | Silence Therapeutics | Phase II Clinical Trials |
| LY3819469 | 2022 | Eli Lilly | Phase II Clinical Trials |
| Muvalaplin (AKCEA-APOCIII-LRx) | 2023 | Ionis Pharmaceuticals/Akcea Therapeutics | Phase II Clinical Trials |
| TQJ221 (IONIS-DGAT2-LRx) | 2021 | Ionis Pharmaceuticals/Akcea Therapeutics | Phase II Clinical Trials |
| ARO-LPA | 2020 | Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals | Phase II Clinical Trials |
| LY3403162 | 2019 | Eli Lilly | Phase I Clinical Trials |
| AMG-596 | 2019 | Amgen | Phase I Clinical Trials |
| IONIS-APO(a)-LRx | 2018 | Ionis Pharmaceuticals/Akcea Therapeutics | Phase II Clinical Trials |
| AKCEA-APO(a)-LRx | 2016 | Ionis Pharmaceuticals/Akcea Therapeutics | Phase I Clinical Trials |
| ISIS-681257 | 2015 | Ionis Pharmaceuticals/Akcea Therapeutics | Preclinical Development |
| Lomitapide (Juxtapid) | 2012 | Aegerion Pharmaceuticals | Approved for Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia |
| Anacetrapib (Cetpvan) | 2010 | Merck | Withdrawn from Market |
| Niacin | 1950s | Various | Available Over-the-Counter |
Notes:
- This list includes both approved and investigational drugs.
- The stage of development indicates the current status of the drug’s clinical testing.
- Some drugs may have multiple names or development codes.
- New drugs are constantly being developed, so this list may not be exhaustive.
A few of these newer drugs are approved for human use in USA and other countries. Niacin is one of the products that has lp(a) lowering properties. The other approved drugs are listed in Table 2
TABLE 2
Approve Drugs for lowering lipoprotein(a):
| Name of Drug | Year | Company |
| Niacin (vitamin B3) | 1937 | Various |
| Lomitapide | 2012 | Aegerion Pharmaceuticals |
| Evolocumab (Repatha) | 2015 | Amgen |
| Alirocumab (Praluent) | 2015 | Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals |
| Bococizumab (Nexletol) | 2017 | Pfizer |
There are 4 drugs approved for clinical use, namely Lomitapide. Evolocumab, Alirocumab and Bococizumab. There are many other products under different stages of development.
Lomitapide
Chemical name: (2S,4S)-N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-phenyl-3-thiazolidine carboxamide
Structure:
Use: Lomitapide is used as a lipid lowering agent for lowering LDL cholesterol. It seems it is not targeted to lower lipoprotein(a).
——————————————————————————————————————————-
Evolocumab (Repatha)
Chemical Name: Human monoclonal antibody (IgG2 kappa) against proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9)
Structure:
Brand Name: Repatha
Developer: Amgen
Summary: This is not a chemical product. It is a biotechnology product and is a complex protein molecule. Evolocumab is a PCSK9 (proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9) inhibitor antibody used as an adjunct to LDL cholesterol reducing therapies, aiding in the prevention of cardiovascular events and cardiovascular revascularization procedures.
Indications: Evolocumab is indicated in adult patients with established cardiovascular disease to reduce the risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, and coronary revascularization. It is also indicated as an adjunct to diet, alone or in combination with other hypolipidemic treatments, in adults with primary hyperlipidemia (and in pediatric patients ≥10 years old with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia) to reduce LDL-C. In addition, it is indicated adjunctly to other hypolipidemic treatments in patients ≥10 years old with homozygous familiar hypercholesterolemia to reduce LDL-C.
Associated Conditions: Coronary Revasculrization, Myocardial Infraction, Stroke, Increase in serum low density lipoprotein (LDL)
—————————————————————————————————————————-
Alirocumab (Praluent)
Chemical Name: Human monoclonal antibody (IgG1 kappa) against PCSK9
Structure:
Brand Name: Praluent
Company: Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals
Summary: Alirocumab is a PCSK9 inhibitor used as an adjunct to manage heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia or clinical atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in patients who require additional lowering of LDL-cholesterol (LDL-C).
Indications:
Alirocumab is an antibody eliciting proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitor activity that is indicated for:
(i) use in reducing the risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, and unstable angina requiring hospitalization in adults with established cardiovascular disease 4, and/or
(ii) use as an adjunct to diet or use alone or in combination with other lipid-lowering therapies (statins, ezetimibe, for example) for the treatment of adults with primary hyperlipidemia (including heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia) to reduce low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels in the body
Associated Conditions: Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia (HeFH), Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolaemia (HoFH), Myocardial Infarction, Stroke, Unstable Angina Pectoris and Primary Hyperlipidemia
Bococizumab (Nexletol)
Chemical Name: Humanized monoclonal antibody (IgG1 kappa) against PCSK9
Structure: Complex protein structure similar to Alirocumab and other PCSK9 inhibitore
Brand Name: Nexletol
Company: Pfizer
Summary: Bococizumab has been used in trials studying the treatment and prevention of Dyslipidemia, Hyperlipidemia, Hypercholesterolemia, Cardiovascular Disease, and Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia.
Mechanism of action of Evolocumab, Alirocumab and Bococizumab:
All these products are fully human IgG1 monoclonal antibody that binds and inhibit proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9), an enzyme found to have “gain of function” mutations in autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia.
PCSK9 is secreted by the liver and typically binds to the LDL receptors in serum and marks them for lysosomal degradation.
In result, the LDL receptors are not able to recycle to the plasma membrane, reducing their binding to LDL-C and therefore reducing the clearance of LDL-C from plasma.
Therefore by inhibiting PCSK9’s actions, these PCSK9 inhibitors allows for more LDL-C reuptake by the liver and facilitates a higher rate of clearance.
Lower LDL cholesterol concentrations are associated with a reduced risk of coronary heart disease. This means slowing down the rate of atherosclerosis.
Muvalaplin (LY3473329)
First oral treatment for Lipoprotein(a) shows significant cholesterol reduction: https://www.news-medical.net/news/20230828/First-oral-treatment-for-Lipoprotein(a)-shows-significant-cholesterol-reduction.aspx
———————————————————————————————————————————
Resources
Evolocumab: https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB09303
Alirocumab: https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB09302
Bococizumab: https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB12456
PubChem: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
DrugBank: https://go.drugbank.com/
Targeted Treatment against Lipoprotein (a): The Coming Breakthrough in Lipid Lowering Therapy https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9781646/
Modern Approaches to Lower Lipoprotein(a) Concentrations and Consequences for Cardiovascular Diseases https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8469722/
Muvalaplin and Olpasiran Show Promise in Lowering Lp(a) https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/996568?form=fpf
Lipoprotein(a) in clinical practice https://www.acc.org/Latest-in-Cardiology/Articles/2019/07/02/08/05/Lipoproteina-in-Clinical-Practice
Effects of Lipid-Modifying and Other Drugs on Lipoprotein(a) Levels—Potent Clinical Implications https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10222947/ [lomitapide, Mipomersan, Mempedoic acid]
Mipomersan https://go.drugbank.com/unearth/q?searcher=drugs&query=mipomersan
Chronic illness treatment https://www.lybrate.com/topic/chronic-illness

